BLOCKCHAIN
BLOCKCHAIN
It’s been over ten years now since Satoshi Nakamoto
published the Bitcoin. In that time, blockchain technology has made
significant, affecting thousands, if not millions, of people around the
world. The 21st century is all about technology. With the increasing need for
modernization in our day-to-day lives, people are open to accepting new
technologies. From using a remote for controlling devices to using voice notes
for giving commands; modern technology has made space in our regular lives.
Technologies like augmented reality and IoT that have gained pace in the past
decade and now there’s a new addition to the pack i.e. Blockchain
Technology.
WHAT IS BLOCKCHAIN?
A blockchain, originally divided into two parts block chain, corresponds to two words,
which is a growing list of records, called blocks, that are linked using cryptography. Each
block contains a cryptography hash of
the previous block.
WHY BLOCKCHAIN
Blockchain was
invented by a person (or group of people) using the name Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008 to serve as the public transaction ledger of the cryptocurrency bitcoin. The identity of Satoshi Nakamoto is unknown. The
invention of the blockchain for bitcoin made it the first digital currency to
solve the double-spending problem without the need for a trusted authority or
central server. The bitcoin design has inspired other applications, and
blockchains that are readable by the public are widely used by cryptocurrencies. Blockchain is considered a type of payment rail. Private blockchains have been proposed for business use.
Sources such as Computerworld called the
marketing of such blockchains without a proper security model.
Types of blockchain!
- Public blockchain
A public blockchain has
absolutely no access restrictions. Anyone with an Internet connection can send transactions to
it as well as become a validator (i.e.,
participate in the execution of a consensus
protocol). Usually, such networks offer economic incentives for those who secure
them and utilize some type of a Proof of Stake or Proof of Work algorithm. Some of the largest, most
known public blockchains are the bitcoin blockchain and the Ethereum
blockchain.
- Private blockchains
A private blockchain is
permissioned. One
cannot join it unless invited by the network administrators. Participant and
validator access is restricted.
- Hybrid blockchains
POPULAR APPLICATIONS!
- Smart contracts
- Government Elections
- Identity management
- Intellectual Property Protection
Identity management
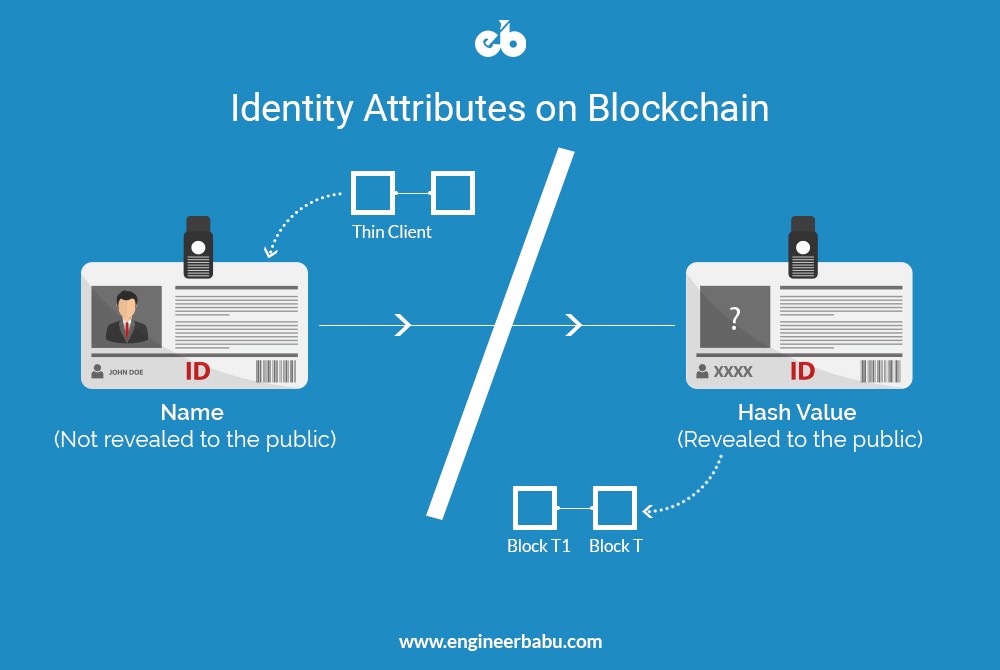
The world is getting more digitized with every passing day. Consider financial transactions happening online for instance, you can easily login with your credentials and security pin to access your funds. However, in this case, no one can ensure the identity of the person taking out the money. If your username and password are hacked by someone, there’s no way to secure your money.
The need of the hour is to have a system that manages individual identification on the web. The distributed ledger technology used in blockchains offers you advanced methods of public-private encryption using which, you can prove your identity and digitize your documents. This unique secure identity can work as a savior for you while conducting any financial transactions or any online interactions on a shared economy. Moreover, the gap between different government bodies and private organizations can be filled through a universal online identity solution that blockchain can provide.
Its uses?
- Cryptocurrencies
- Smart contracts
- Financial services
- Video games
- Supply chain
Why to know about blockchain?
In our field of CSE the updations towards the infield
knowledge is the main key according to me the official and non-official use of
blockchain would be done in upcoming days and why it is coming in use nowadays that’s
just because the data is stored in the different blocks where when a hacker interrupts
the transaction he gets only of the 7% part of the transaction or process where
till the use, it changes. On another step, the user knows the private key whether
the system also don’t know about the private key so decryption doesn’t take
place.






Well done
ReplyDeletethank you
DeleteIs requires deep understanding and research before writing about these kind of topics. Really appreciate the hard work that you have put behind in writing this article! Keep writing brother! Eagerly waiting for your next one!
ReplyDeleteTotally agree with u
Deletebest complement ever heard bro... thanx alot
DeleteInteresting topic bro 😃🔥🔥🔥
ReplyDeletethanks brother
DeleteBrooo....Nailed It🙌🙌
ReplyDeletethanks brother
Delete